Tá riachtanais chomhlíonta ar leith ag gach tír nach mór cloí leo más mian leat do tháirgí a dhíol ansin. Má theipeann ort cloí leis, is féidir fíneálacha airgeadais, aisghairmeacha táirgí, agus fiú príosúnacht a bheith mar thoradh air. Mar sin, cé na riachtanais chomhlíonta a chaithfidh tú a mheas chun rochtain a fháil ar mhargadh nua? Seo na céimeanna is gá duit a ghlacadh:
Céim 1: Sainmhínigh do sprioc -thír
Sainaithin an tír ina bhfuil sé i gceist agat do tháirge a dhíol.
Céim 2: Clúdaigh an reachtaíocht seo a leanas do do sprioc -thír
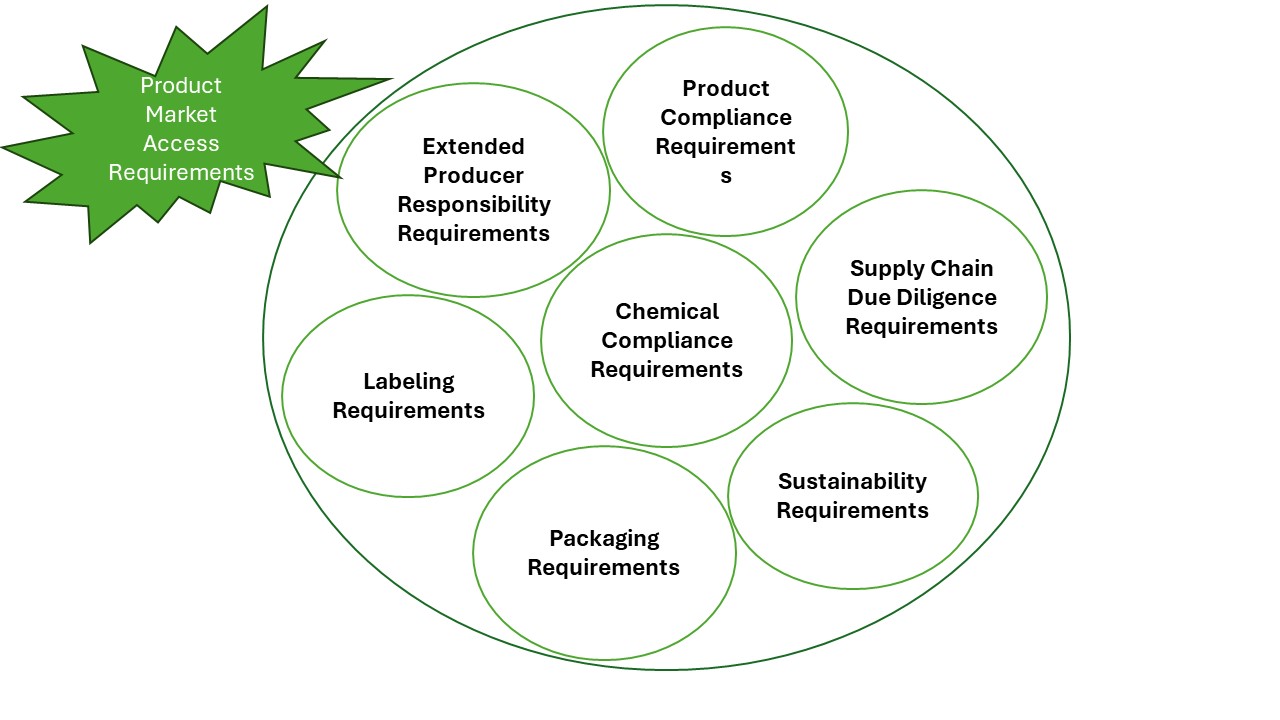
1. Riachtanais um Chomhlíonadh Táirgí
Cinntíonn ceanglais maidir le comhlíonadh táirgí go gcomhlíonann táirge caighdeáin agus rialacháin shonracha atá saincheaptha dá chatagóir. Ráthaíonn na riachtanais seo go bhfuil táirgí sábháilte, iontaofa agus oiriúnach le húsáid.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Caighdeáin Sábháilteachta: Tá comhlíonadh na gcaighdeán sábháilteachta fíorthábhachtach. Tá rialacháin ag gach tír a bhaineann le sábháilteacht leictreach, sábháilteacht mheicniúil, sábháilteacht dóiteáin, agus níos mó. D'fhéadfadh sé go mbeadh deimhnithe mar mharcáil CE san AE, deimhniú OL sna Stáit Aontaithe, nó marcáil CCC sa tSín.
- Sampla: Maidir le fearais leictreacha, a chinntiú go gcomhlíontar caighdeáin chomhoiriúnacht leictreamaighnéadach (EMC) agus treoracha ísealvoltais.
- Deimhnithe a bhaineann go sonrach le tionscal: Ag brath ar an gcatagóir táirgí, d'fhéadfadh go mbeadh gá le deimhnithe sonracha. Mar shampla, ní mór do bhréagáin cloí le caighdeáin a chinntíonn go bhfuil siad sábháilte do leanaí, mar shampla ASTM F963 sna Stáit Aontaithe nó EN 71 san Eoraip.
- Sampla: D'fhéadfadh go mbeadh faomhadh FDA ag teastáil ó fheistí leighis i SAM nó marcáil CE faoi Rialachán Gléas Leighis an AE (MDR).
- Tagarmharcanna feidhmíochta: Ní mór do tháirgí tagarmharcanna feidhmíochta a chomhlíonadh chun a chinntiú go bhfeidhmíonn siad mar a fógraíodh iad. Áirítear leis seo rátálacha éifeachtúlachta fuinnimh, tástálacha marthanachta, agus feidhmíocht dálaí comhshaoil.
- Sampla: B'fhéidir go mbeidh ar fhearais cloí le caighdeáin éifeachtúlachta fuinnimh mar Star Energy i dTreoracha Stáit Aontaithe Mheiriceá nó ERP san AE.
- Caighdeáin Idir -Inoibritheachta: Maidir le táirgí teicneolaíochta, cinntíonn cloí le caighdeáin idir -inoibritheachta comhoiriúnacht le gléasanna agus córais eile. Áirítear leis seo deimhnithe Wi-Fi, comhoiriúnacht Bluetooth, etc.
- Sampla: Cinntigh go bhfuil fóin chliste comhoiriúnach le líonraí agus caighdeáin teileachumarsáide áitiúla.
2. Riachtanais um Chomhlíonadh Ceimiceach
Díríonn riachtanais chomhlíonta ceimiceacha ar rialacháin a bhaineann le húsáid, nochtadh, agus srian ceimiceán i dtáirgí, ag cosaint tomhaltóirí agus an chomhshaoil araon.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Substaintí srianta: Tá liostaí de shubstaintí toirmiscthe nó srianta ag go leor tíortha. Is éard atá i gceist le comhlíonadh ná a chinntiú nach bhfuil ceimiceáin dhíobhálacha i do tháirgí thar theorainneacha incheadaithe. Is sampla suntasach é rialachán sroichte an AE, a chuireann srian ar cheimiceáin áirithe i dtáirgí.
- Sampla: A chinntiú go gcomhlíontar treoir an AE ar threoir na substaintí guaiseacha (ROHS), a chuireann teorainn le húsáid ábhar guaiseach sonrach i dtáirgí leictreacha agus leictreonacha.
- Measúnuithe sábháilteachta ceimiceacha: Cuidíonn measúnuithe sábháilteachta ceimiceacha a dhéanamh le guaiseacha féideartha a bhaineann leis na ceimiceáin a úsáidtear i do tháirgí a aithint. Soláthraíonn bileoga sonraí sábháilteachta (SDS) faisnéis faoi láimhseáil shábháilte, stóráil agus diúscartha.
- Sampla: SDS a sholáthar do tháirgí ceimiceacha i gcomhréir leis an gcóras comhchuibhithe domhanda (GHS) aicmiú agus lipéadú ceimiceán.
- Lipéadú agus nochtadh: Éilíonn comhlíonadh lipéadú agus nochtadh cuí ar ábhar ceimiceach. Áirítear leis seo faisnéis shoiléir a sholáthar faoi chomhábhair ghuaiseacha agus réamhchúraimí riachtanacha.
- Sampla: Ní mór do tháirgí cosmaideacha san AE cloí leis an Rialachán Táirgí Cosmaideacha (CE) Uimh. 1223/2009, a éilíonn liosta comhábhar iomlán agus lipéadú sonrach do ailléirginí.
- Rialacháin Táirgí Biocidal: Má tá substaintí bithmhaitheacha i do tháirge (m.sh., dífhabhtóirí), tá gá le comhlíonadh rialacháin cosúil le Rialachán Táirgí Bithmhaideach an AE (BPR).
- Sampla: Cinntigh go gcomhlíonann táirgí dífhabhtáin caighdeáin éifeachtúlachta sonracha agus riachtanais lipéadaithe.
3. Riachtanais Lipéadaithe
Is éard atá i gceist le riachtanais lipéadaithe ná caighdeáin a chinntíonn go gcuireann táirgí faisnéis riachtanach in iúl do thomhaltóirí, amhail rabhaidh sábháilteachta, treoracha úsáide, agus faisnéis chothaithe.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Riachtanais Teanga: Caithfidh lipéid a bheith i dteanga / i dteanga oifigiúil an spriocmhargaidh. Áirítear leis seo na treoracha, na rabhaidh agus na tuairiscí go léir lena chinntiú go dtuigeann tomhaltóirí sonraí táirge.
- Sampla: I gCeanada, ní mór lipéid a bheith i mBéarla agus i bhFraincis araon.
- Rabhaidh agus siombailí sábháilteachta: Is éard atá i gceist le comhlíonadh ná rabhaidh agus siombailí sábháilteachta éigeantacha a thaispeáint, amhail picteagraim ghuaise, rabhaidh ailléirge, agus lipéid a oireann don aois.
- Sampla: Ní mór do bhréagáin san AE an marc CE, srianta aoise agus rabhaidh sábháilteachta a thaispeáint.
- Faisnéis Chothaitheach (Táirgí Bia): Maidir le táirgí bia, áirítear le comhlíonadh faisnéis chothaithe, liostaí comhábhar, agus rabhaidh ailléirgin a sholáthar.
- Sampla: Sna Stáit Aontaithe, ní mór do lipéid bia cloí le rialacháin FDA, lena n -áirítear fíricí cothaitheacha, méideanna fónamh, agus dearbhuithe comhábhair.
- Socrúchán Cód Barcode agus QR: Cinntíonn cloí le caighdeáin le haghaidh socrúcháin bharrachód agus QR cód scanadh éifeachtach agus rianú táirgí ar fud an tslabhra soláthair.
- Sampla: Is minic a úsáidtear caighdeáin GS1 maidir le socrúchán barrachód le haghaidh táirgí miondíola.
- Éicea-lipéid agus Deimhnithe: D'fhéadfadh go mbeadh gá le héicea-lipéid agus deimhniúcháin ar leith ag baint le táirgí a éilíonn sochair chomhshaoil, amhail an t-éiceaball nó an réalta fuinnimh AE.
- Sampla: Cinntigh go dtaispeánann fearais atá tíosach ar fhuinneamh lipéid chuí fuinnimh.
4. Riachtanais Pacáistithe
Díríonn riachtanais phacáistithe ar ábhair agus ar dhearadh pacáistithe chun caighdeáin chomhshaoil agus sábháilteachta a chomhlíonadh agus ag an am céanna sábháilteacht tomhaltóirí agus sláine táirgí a chinntiú.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Srianta ábhair: Is éard atá i gceist le comhlíonadh ná ábhair phacáistithe a úsáid a chomhlíonann caighdeáin sábháilteachta agus comhshaoil, mar shampla plaistigh díobhálacha nó miotail throma a sheachaint.
- Sampla: Cuireann Treoir Dramhaíola Pacáistithe agus Pacáistithe an AE srian ar úsáid miotal trom áirithe i bpacáistiú.
- Athchúrsáil agus bith -dhíghrádú: Cinntíonn cloí le rialacháin a chuireann athchúrsáil agus bith -dhíghrádú chun cinn go bhfuil tionchar íosta comhshaoil ag ábhair phacáistithe.
- Sampla: Tá úsáid ábhar in -athchúrsáilte i bpacáistiú ag teacht le spriocanna inbhuanaitheachta i go leor tíortha.
- Lipéadú ábhair phacáistithe: Ní mór lipéid shoiléire a bheith san áireamh sa phacáistiú a léiríonn an cineál ábhar a úsáidtear agus treoracha athchúrsála.
- Sampla: Bain úsáid as siombailí chun comhpháirteanna in -athchúrsáilte agus treoirlínte diúscartha a léiriú.
- Dearadh agus Sábháilteacht: Ní mór do dhearadh pacáistithe an táirge a chosaint ó dhamáiste agus sábháilteacht tomhaltóirí a chinntiú le linn láimhseála agus úsáide.
- Sampla: Pacáistiú atá frithsheasmhach in aghaidh leanaí le haghaidh cógaisíochta agus ceimiceán tí.
- Pacáistiú laghdaithe agus íoslaghdú dramhaíola: D'fhéadfadh rialacháin pacáistiú a spreagadh chun dramhaíl a laghdú, réitigh phacáistithe atá neamhdhíobhálach don chomhshaol a chur chun cinn.
- Sampla: Dearadh pacáistithe atá neamhdhíobhálach don chomhshaol a chur i bhfeidhm chun ailíniú le Plean Gníomhaíochta Geilleagar Ciorclach an AE.
5. Riachtanais Freagrachta um Freagracht an táirgeora leathnaithe (EPR)
Coinníonn riachtanais Freagrachta an táirgeora leathnaithe (EPR) táirgeoirí atá freagrach as saolré iomlán a gcuid táirgí, lena n -áirítear diúscairt agus athchúrsáil, chun bainistíocht dramhaíola inbhuanaithe a chur chun cinn.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Scéimeanna Tógtha Táirgí: Is éard atá i gceist le comhlíonadh ná scéimeanna glactha a chur i bhfeidhm inar féidir le tomhaltóirí táirgí a úsáidtear a thabhairt ar ais le haghaidh athchúrsála nó diúscartha.
- Sampla: B'fhéidir go mbeidh ar mhonaróirí leictreonaice cláir athchúrsála r-dhramhaíola a bhunú.
- Oibleagáidí Bainistíochta Dramhaíola: Ní mór do tháirgeoirí cloí le rialacháin maidir le bainistiú dramhaíola, ag cinntiú go bhfuil diúscairt agus athchúrsáil cheart táirgí agus pacáistiú ann.
- Sampla: Ní mór do tháirgeoirí ceallraí san AE cloí leis an treoir cadhnraí, bailiú agus athchúrsáil chuí a chur chun cinn.
- Tuairisciú agus doiciméadú: Áirítear le cloí le riachtanais EPR taifid a choinneáil agus tuairisciú ar iarrachtaí athchúrsála agus tionscnaimh bainistíochta dramhaíola.
- Sampla:B'fhéidir go mbeidh ar chuideachtaí tuarascálacha bliantúla a chur isteach maidir le rátaí bailithe agus athchúrsála dramhaíola.
- Comhoibriú le heagraíochtaí údaraithe: Cinntíonn comhpháirtíocht le heagraíochtaí bainistíochta dramhaíola údaraithe go gcomhlíontar rialacháin áitiúla EPR.
- Sampla: Comhoibriú le scéimeanna comhlíonta pacáistithe údaraithe le haghaidh bainistíochta dramhaíola cuí.
- Freagracht Airgeadais: Féadfaidh táirgeoirí freagracht airgeadais a bheith acu as bainistíocht dramhaíola, ag cur le cláir agus tionscnaimh athchúrsála.
- Sampla: D'fhéadfadh go mbeadh ar chuideachtaí táillí a íoc chun tacú le bonneagar athchúrsála áitiúil.
6. Riachtanais Inbhuanaitheachta
Díríonn riachtanais inbhuanaitheachta ar chleachtais atá neamhdhíobhálach don chomhshaol a chur chun cinn, amhail treoracha éicea-dheartha agus pasanna táirgí digiteacha, chun táirgí inbhuanaithe agus trédhearcacha a chruthú.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Treoracha éicea-dheartha: Is éard atá i gceist le comhlíonadh táirgí a dhearadh le hinbhuanaitheacht san áireamh, mar shampla ídiú fuinnimh a íoslaghdú agus ábhair inbhuanaithe a úsáid.
- Sampla: Leagann treoir éicea-dheartha an AE caighdeáin éifeachtúlachta fuinnimh do tháirgí éagsúla.
- Pasanna Táirgí Digiteacha: Tugann cur i bhfeidhm pasanna táirgí digiteacha faisnéis do thomhaltóirí faoi inbhuanaitheacht táirgí, lena n -áirítear tionscnamh, ábhair, agus tionchar saolré.
- Sampla: Bain úsáid as cóid QR chun faisnéis inbhuanaitheachta mhionsonraithe a sholáthar do thomhaltóirí.
- Foinsiú inbhuanaithe: Cinntíonn cloí le rialacháin ábhair a fhoinsiú ó fhoinsí inbhuanaithe agus eiticiúla, rud a laghdaíonn tionchar comhshaoil.
- Sampla: Bain úsáid as ábhair atá foinsithe go hinbhuanaithe agus ailíniú le deimhnithe cosúil le FSC do tháirgí adhmaid.
- Trédhearcacht Lorg Carbóin: Cuidíonn soláthar trédhearcachta maidir le lorg carbóin na dtáirgí le tomhaltóirí roghanna eolasacha a dhéanamh.
- Sampla: Taispeáin lipéid lorg carbóin chun tionchar comhshaoil a thaispeáint.
- Measúnuithe Saolré: Déanann measúnuithe saolré a dhéanamh meastóireacht ar thionchar comhshaoil táirge ó tháirgeadh go diúscairt.
- Sampla: Measúnuithe saolré a dhéanamh chun réimsí a aithint le haghaidh feabhsúcháin inbhuanaitheachta.
7. Slabhra Soláthair Riachtanais díchill chuí
Cinntíonn riachtanais díchill chuí an slabhra soláthair go gcomhlíontar cearta an duine, dlíthe sclábhaíochta nua-aimseartha, agus bearta frith-éillithe, ag cur cleachtais ghnó eiticiúla agus fhreagrach chun cinn.
Príomh -chúinsí:
- Comhlíonadh um Chearta an Duine: Cinntigh go bhfuil meas ag do shlabhra soláthair ar chearta an duine, ag seachaint cleachtais cosúil le saothar leanaí, saothair éigeantach, agus idirdhealú.
- Sampla: Beartais chearta an duine a chur i bhfeidhm agus iniúchtaí a dhéanamh chun measúnú a dhéanamh ar chomhlíonadh sa slabhra soláthair.
- Dlíthe Sclábhaíochta Nua -Aimseartha: Cloí le dlíthe a bhaineann le sclábhaíocht nua -aimseartha, amhail Acht Sclábhaíochta Nua -Aimseartha na Ríochta Aontaithe, ag cinntiú cleachtais chothroma saothair ar fud an tslabhra soláthair.
- Sampla: Cuir clásail frith-sclábhaithe san áireamh i gconarthaí soláthróirí agus i measúnuithe soláthróirí iompair.
- Bearta Frith-Éillithe: Bearta frith-éillithe a chur i bhfeidhm chun cosc a chur ar chleachtais breabaireachta agus mí-eiticiúla laistigh de do shlabhra soláthair.
- Sampla: Beartais agus cláir oiliúna frith-éillithe a bhunú d'fhostaithe agus do chomhpháirtithe.
- Iniúchtaí Slabhra Soláthair: Cabhraíonn iniúchtaí agus measúnuithe rialta le rioscaí a aithint agus le comhlíonadh na gceanglas díchill chuí a chinntiú.
- Sampla: Déan iniúchtaí a dhéanamh chun comhlíonadh le caighdeáin foinsithe eiticiúla a fhíorú.
- Cód Iompair Soláthraithe: Leagann bunú cód iompair soláthróra caighdeáin eiticiúla agus comhlíonta do sholáthraithe, ag cur cleachtais ghnó freagracha chun cinn.
- Sampla: Cód iompair a fhorbairt ag cur síos ar ionchais do sholáthraithe agus do chomhpháirtithe.
Céim 3: Fan Nuashonraithe
An tábhacht a bhaineann le fanacht ar an eolas
I margadh domhanda an lae inniu, tá rialacháin ag athrú i gcónaí mar gheall ar dhul chun cinn teicneolaíochta, athruithe ar ionchais tomhaltóirí, ábhair imní chomhshaoil, agus athruithe polaitiúla. Dá bhrí sin, ní mór do ghnólachtaí a bheith airdeallach agus réamhghníomhach chun monatóireacht a dhéanamh ar nuashonruithe rialála chun gaistí féideartha a sheachaint.
Príomhchúiseanna le fanacht cothrom le dáta
- Pionóis agus fíneálacha a sheachaint:
- Iarmhairtí airgeadais:Is féidir le neamhchomhlíonadh pionóis airgeadais suntasacha, fíneálacha, nó fiú caingean dlí a bheith mar thoradh air. Cuidíonn tuiscint ar na hathruithe rialála is déanaí leis na rioscaí seo a mhaolú.
- Sampla: Is féidir le cuideachta a dhíolann leictreonaic san AE fíneálacha a fháil mura gcomhlíonann sí treoracha nuashonraithe ROHS a chuireann srian ar shubstaintí guaiseacha.
- Riachtanais Iontrála Margaidh: Cinntíonn fanacht cothrom le dáta go leanann do tháirgí ag freastal ar riachtanais iontrála an mhargaidh, rud a chuireann cosc ar bhriseadh i ndíolacháin.
- Sampla: Ní mór do chuideachta bia atá ag leathnú isteach i réigiún nua a lipéadú a oiriúnú chun rialacháin faisnéise cothaithe áitiúla a chomhlíonadh.
- Iontaobhas Tomhaltóirí: Tógann comhlíonadh na rialachán is déanaí muinín le tomhaltóirí, a bhfuil súil acu go gcomhlíonfaidh táirgí caighdeáin ard sábháilteachta agus eiticiúla.
- Sampla: Ní mór do bhranda faisin atá tiomanta do chleachtais inbhuanaithe fanacht ar an eolas faoi rialacháin nua teicstíle chun a íomhá atá neamhdhíobhálach don chomhshaol a choinneáil.
- Nuálaíocht agus iomaíochas: Trí bheith feasach ar threochtaí rialála is féidir le gnólachtaí iad féin a nuáil agus iad féin a idirdhealú ó iomaitheoirí.
- Sampla: D'fhéadfadh cuideachta ardteicneolaíochta rialacháin nua príobháideachta sonraí a ghiaráil chun a thairiscintí táirge a fheabhsú, ag soláthar breisluach do chustaiméirí.
Straitéisí chun fanacht nuashonraithe
- Monatóireacht a dhéanamh ar chomhlachtaí rialála:
- Údaráis dhomhanda agus áitiúla: Coinnigh súil ar chomhlachtaí rialála ábhartha amhail an Coimisiún Eorpach, FDA, agus gníomhaireachtaí náisiúnta eile le haghaidh nuashonruithe.
- Sampla: Liostáil le nuachtlitreacha nó le foláirimh ó chomhlachtaí rialála i do thionscal chun nuashonruithe tráthúla a fháil.
- Líonraí Tionscail: Bí páirteach i gcumainn tionscail agus i ngrúpaí trádála a thugann léargas ar athruithe rialála agus ar threochtaí tionscail.
- Sampla: Is féidir le ballraíocht i gcomhlachais mar an Cumann Teicneolaíochta Tomhaltóirí rochtain a sholáthar ar thuarascálacha tionscail agus anailís shaineolach.
- Bogearraí comhlíonta: Infheistiú i mbogearraí bainistíochta comhlíonta a dhéanann monatóireacht a dhéanamh ar mhonatóireacht agus a thugann foláireamh duit maidir le hathruithe rialála.
- Sampla: Bain úsáid as ardáin cosúil le comhlíonadh aontaithe chun riachtanais chomhlíonta a rianú i réigiúin éagsúla.
- Comhairle ghairmiúil: Dul i dteagmháil le saineolaithe dlí agus le comhairleoirí comhlíonta a dhéanann speisialtóireacht i do thionscal chun a chinntiú go dtuigeann tú agus go gcuireann tú athruithe riachtanacha i bhfeidhm.
- Sampla: Oibriú le foirne dlí chun rialacháin chasta a léirmhíniú agus a n -impleachtaí do do ghnó.
- Oiliúint fostaithe: Seisiúin oiliúna rialta a dhéanamh d'fhostaithe chun iad a choinneáil ar an eolas faoi nuashonruithe rialála agus cleachtais chomhlíonta.
- Sampla: Modúil ríomhfhoghlama a chur i bhfeidhm a dhíríonn ar riachtanais nua comhlíonta chun feasacht agus cloí foirne a chinntiú.
- Imeachtaí Tionscail: Freastal ar cheardlanna, comhdhálacha, agus seimineáir ghréasáin a dhíríonn ar threochtaí rialála agus ar straitéisí comhlíonta.
- Sampla: Páirt a ghlacadh in imeachtaí cosúil leis an gCruinniú Mullaigh um Chomhlíonadh Domhanda chun foghlaim ó shaineolaithe agus ó líonra le comhghleacaithe.
Conas is féidir le comhlíonadh margaíocht cabhrú
I Comhlíonadhmharket a chomhlíonadh , speisialtóireacht againn le cuidiú le gnólachtaí na castachtaí a bhaineann le comhlíonadh rialála a dhéanamh. Soláthraíonn ár bhfoireann gairmithe réitigh saincheaptha chun a chinntiú go bhfanfaidh tú ar an eolas agus go gcomhlíonann tú i do sprioc -mhargaí.
- Treoir shaineolach:
- Anailís dhomhain: Déanann ár bhfoireann anailís chríochnúil ar riachtanais rialála a bhaineann go sonrach le do thionscal agus do sprioc -thír, ag cinntiú go dtuigeann tú cad is gá le haghaidh comhlíonta.
- Sampla: Is féidir linn tuairiscí mionsonraithe a sholáthar ar rialacháin nua um chomhlíonadh ceimiceach san AE, ag cur síos ar chéimeanna le cur i bhfeidhm.
- Straitéisí saincheaptha: Forbraímid straitéisí comhlíonta saincheaptha a thagann le do chuspóirí gnó agus le pleananna iontrála margaidh.
- Sampla: Má tá sé ar intinn agat dul isteach i margaí éagsúla, cuirimid réitigh chomhlíonta il-thíre ar fáil a thugann aghaidh ar rialacháin uathúla gach réigiúin.
- Nuashonruithe leanúnacha:I measc ár seirbhísí tá monatóireacht leanúnach ar athruithe rialála, ag cinntiú go bhfaigheann tú nuashonruithe agus moltaí tráthúla.
- Sampla: Faigh feasacháin chomhlíonta míosúla leis na hathruithe is déanaí i rialacháin phacáistithe a théann i bhfeidhm ar do thionscal.
- Ceardlanna agus Seimineáir: Cuirimid cláir oiliúna agus ceardlanna ar fáil chun oideachas a chur ar do fhoireann ar na cleachtais chomhlíonta is déanaí agus na nuashonruithe rialála.
- Sampla: Bí i do sheimineáir ghréasáin ar riachtanais díchill chuí an slabhra soláthair chun tuiscint agus ullmhacht do fhoireann a fheabhsú.
- Uirlisí nuálacha: Giarála ár n -uirlisí bainistíochta comhlíonta chun do phróisis a shruthlíniú agus a chinntiú go gcloítear gan uaim le rialacháin.
- Sampla: Tairgeann ár n -ardán foláirimh agus dashboards uathoibrithe chun comhlíonadh a rianú ar fud do línte táirge agus do gheografaíochtaí.
- Bainistíocht Riosca Réamhghníomhach: Cabhraímid leat rioscaí comhlíonta a aithint agus straitéisí a fhorbairt chun iad a mhaolú go héifeachtach.
- Sampla: Léiríonn ár Seirbhísí Measúnaithe Riosca réimsí leochaileachta i do shlabhra soláthair, ag soláthar léargais inchaingne chun aghaidh a thabhairt orthu.
Comhroinn le do phobal
Deir
Fág trácht nó cuir ceist